08
Nov
HDPE Pipe Pressure Rating: Understand the Numbers
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are integral to numerous industrial, municipal, and domestic applications, valued for their durability and flexibility. However, understanding their pressure rating is crucial to ensure safe and effective operation. This article will elucidate the concept of HDPE pipe pressure rating, discuss the common numbers associated with these ratings, and provide a pragmatic guide for selecting the appropriate pressure rating for specific projects.
Sizing Guide: HDPE Pipe Pressure Rating
The Fundamentals of Pressure Rating
The pressure rating of an HDPE pipe indicates the maximum pressure that the pipe can handle at a specific temperature. It’s a measure of performance and safety. The rating is usually expressed in pounds per square inch (psi) or bars.
Common Pressure Rating Numbers
The typical pressure ratings for HDPE pipes range from PN6, which stands for “Pressure Nominal 6 bar,” to PN20, indicating a nominal pressure of 20 bars at 20°C. Other common ratings include:
- PN10
- PN12.5
- PN16

Deciphering the Numbers
The numbers in the pressure ratings correlate to the maximum operational pressures at 20°C, with the PN number indicating the pressure in bars. For example:
| PN Rating | Max Operational Pressure (at 20°C) |
| PN6 | 6 bar (87 psi) |
| PN10 | 10 bar (145 psi) |
| PN12.5 | 12.5 bar (181 psi) |
| PN16 | 16 bar (232 psi) |
| PN20 | 20 bar (290 psi) |
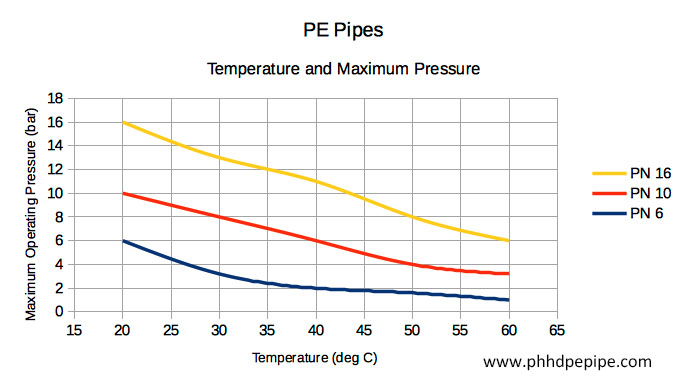
Temperature and Pressure Rating
It’s important to note that the pressure rating decreases as the temperature increases. Manufacturers typically provide a de-rating factor to adjust the pressure rating at various temperatures.
Choosing the Right HDPE Pipe Pressure Rating for Your Project
- Understand the Operating Conditions: Analyze the maximum pressure and temperature conditions your system will face.
- Consider Safety Factors: Always choose a pipe with a pressure rating higher than the maximum operating pressure to incorporate a safety margin.
- Consult the De-rating Factor: Adjust the pressure rating according to the temperature of your application.
For a visual aid, a chart could illustrate how pressure rating changes with temperature:
| Temperature (°C) | De-Rating Factor |
| 20 | 1.00 |
| 25 | 0.93 |
| 35 | 0.87 |
| 45 | 0.82 |
In conclusion, comprehending HDPE pipe pressure ratings is vital for the safety and efficiency of your piping system. With a clear understanding of the numbers and factors affecting these ratings, industry professionals can make informed decisions, ensuring the longevity and reliability of their HDPE piping installations.
Remember to always consult with a qualified engineer or the HDPE pipe manufacturer to ensure that the chosen pressure rating is appropriate for your specific application and that all local codes and regulations are met. By following these guidelines, you will be able to select the most suitable HDPE pipe pressure rating for your project’s needs.

